Lump Behind the Ear
It might a bit frightening to find a lump behind the ear. The lumps can be small or large, and painful or painless. There are several conditions that can cause both large and small lumps behind the ear. While most causes are not serious, and do not need any active treatment, some others may need medical attention. Let us have a look at the possible causes and the different ways to treat the lumps.
Causes of Lumps Behind the Ear
Dermatitis
The build-up of dead or waxy skin cells as a result of dermatitis can cause a lump behind the ear. These signs are usually accompanied by the flaking of dry skin, inflammation, swelling, and redness. Seborrheic dermatitis is a common form of dermatitis that can cause a lumps behind the ears, especially in patients with epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and AIDS. It is usually triggered by a stressful situation, or climatic changes. Dermatitis can also occur due to the neurological conditions, or fungal infections.
The ear lumps caused by dermatitis can be treated with topical creams and lotions containing corticosteroids like hydrocortisone and betamethasone. These medications help to reduce the discomfort and itching. The lumps caused by a fungal infection can be managed with the help of oral and topical antifungal medications like Ciclopirox and Ketoconazole. A soothing bath using uncooked oatmeal or baking soda can also assist in treating bumps behind the ear.
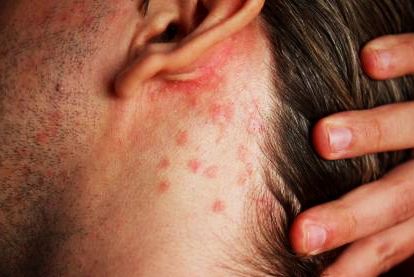
Seborrheic dermatitis with small lumps behind the ear.
Allergies
An allergy is another factor for what causes a lump behind the ear, especially a painful and itchy one. The swelling may occur due to an allergy from ear accessories, perfumes, or even cosmetics. The best way to prevent this is to identify the allergen and then, stop its use. The allergen can be identified by keeping a diary in which you can note down the occurrence of the symptoms and the use of particular cosmetic, jewelry or perfume and then, relate the both to know what exactly caused the lump behind the ear and itching. Insect bites can also cause allergic reactions, and what may at first feel like an innocent pea sized lump can swell up to a big bump.
Swollen Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes can cause lumps behind the ear, which are soft, tender, and painful. An enlarged lymph node can be a sign of an infection in the ears or the area surrounding them. Some other conditions like Streptococcal sore throat, common cold, and sinusitis can also cause the lymph nodes to swell. In case of a generalized infection, there can be lumps behind both ears along with severe weakness, and fever.
A lump behind the ear caused by these infections can be managed using antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory medications. The anti-inflammatory medications help to relieve the pain and swelling while the antibiotics destroy the bacteria responsible for the infection. Sore throat, sinusitis, and common cold can be treated by gargling with warm salt water.
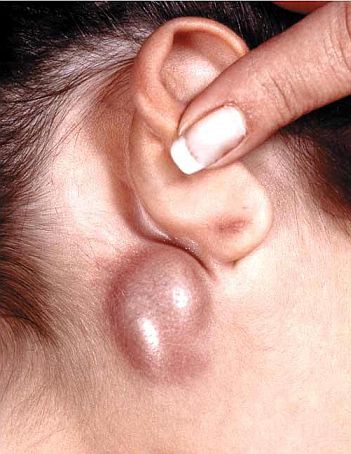
Big lump behind the ear caused by a swollen lymph node
Mastoiditis
Another reason for what causes lumps behind the ear is mastoiditis. It is an infective disorder affecting the mastoid bone located behind the ear. The infection is usually secondary in nature that has spread from an infection in the middle ear or throat. The infection results in the formation of a swollen lump behind the ear by causing inflammation and structural disruptions in the mastoid bone. It may also cause redness, suppuration, ear pain, and swelling along with fever, irritability, headache, and hearing loss.
Mastoiditis can be treated using oral or intravenous antibiotics like Ceftriaxone together with antibiotic ear drops. Some people say that putting few drops of a strained mixture of garlic and olive oil into the ear can also help to relieve the sore lump behind the ear. In severe cases of mastoiditis, surgery is needed to remove the lump behind the ear.
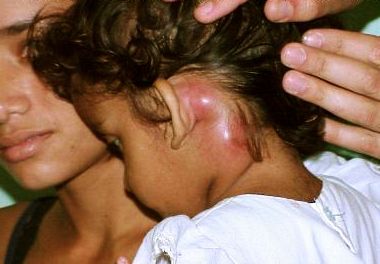
Child with mastoiditis causing a painful lump behind the left ear.
Acne
Acne is the most common skin condition affecting young adults at the age of puberty. It leads to the formation of whiteheads, blackheads, papules, pustules, and small nodules on the skin. In some cases, a lump on the skull behind the ear can be a simple acne eruption. The lump is caused by the hormonal changes occurring in the body during puberty, stress, unusually high levels of androgens, an infection, or even genetic predisposition. Acne lumps can actually appear anywhere behind the ear and they are often painless.
Acne can be treated using medicines containing retinoid (A form of Vitamin A) or benzoyl peroxidase. In case of severe hormonal imbalance, an anti-androgenic hormonal therapy can be prescribed. Oftentimes, this type of condition goes away by itself, just make sure you wash and clean the infected area thoroughly.
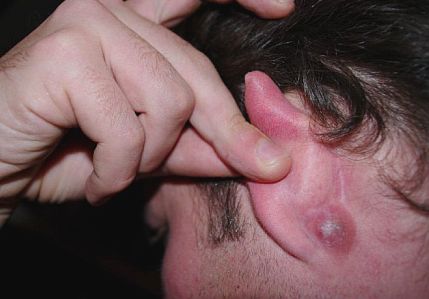
A pimple behind the ear
Cysts
A large or a small painful lump behind the ear can be a cyst. Cysts are fluid-filled bumps that are formed due to several reasons. They are sometimes formed due to the blocked sebaceous glands. These cysts are usually accompanied by the build-up of sebum, in which case they are referred to as a sebaceous cyst. A cartilage piercing bump behind the ear can be the result of a cyst that has burst. An epidermal cyst is made of accumulated keratin, in which case the lumps are formed behind the ears as well as the other body parts. These cysts may get infected and fester.
A cyst can be treated using anti-inflammatory agents, antibiotics, and hydrogen peroxide gels. Warm compresses and heating pads can help to drain the pus and provide relief from the pain. Surgical excision of the cyst or laser therapy may be recommended in severe cases.
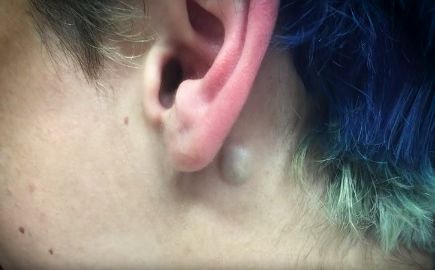
A small cyst close to the earlobe.
Abscess
An itchy lump behind the ear may be due to an infection that has turned into an abscess. An abscess is an enclosed “capsules” with a wall that is filled with pus. An abscess can also develop around a foreign body or from an existing cyst. The treatment involves the use of antibiotics or a surgical excision.
Benign Tumor
A benign tumor may become evident as a lump behind the ear. The swelling is usually soft, painless, and movable. The tumors that can cause a hard painful lump behind the ear include those arising from the salivary glands that have spread to the part behind the ears. These painless tumors may or may not increase in size. A tumor that grows on the mastoid bone is called cholesteatoma. This malformation can destruct the tissues near the ears and cause hearing loss, tinnitus (an abnormal ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears), dizziness, and drainage in the ear.
A benign tumor pose a lower health risk than malignant tumors. Benign tumors behind the ear may grow slowly, but can disappear on their own. Surgical excision may be required for the lump that hurts and makes the jaw movement difficult.

A tumor behind the ear may grow slowly over time.
Cancer
A lump behind the ear can be a malignant growth due to the cancer of salivary glands or the skin. These lumps are usually painless and can grow larger over time. They can be treated with chemotherapy drugs, radiation therapy, surgical excision or a combination of these. The treatment option is based on the stage of the cancer and the extent of its spread.
Lipoma
Lipoma is a swelling caused by the growth of fatty tissues and results in the formation of a lump. The fatty lump often forms between the layers of the skin. These lumps are harmless and can sometimes clear up spontaneously, but in general they tend to grow very slowly. If the lump behind the ear grows or feels bothersome, surgical removal may be an option to opt for.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a noncancerous growth formed due to the abnormal collection of blood vessels. This condition is more common in infants than in adults. It appears as a red/purple bump and is usually found on the skin and the organs, particularly the liver. In rare cases, hemangioma may form behind the ear but they are in most cases benign and harmless.
An early detection of the hemangioma can help to initiate the treatment before any complications arise.
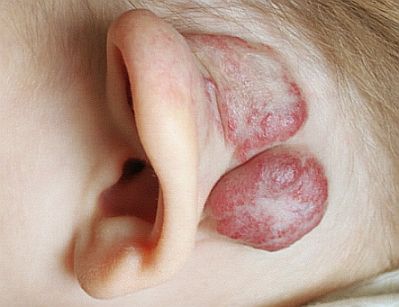
Baby with hamangioma
Keloids
Keloids form when scar tissue overgrows due to a skin injury. This type of condition can form on any part of the body, but when it comes to the ear area, it is often due to piercing. If you have had your ear lobs pierced or an ear cartilage piercing and you are noticng a bump behind the ears, this can be the cause.
Keloid lumps behind the ear are not dangerous and are primarily a cosmetic concern. They can be treated with steroid injections, cosmetic surgery, and compression.
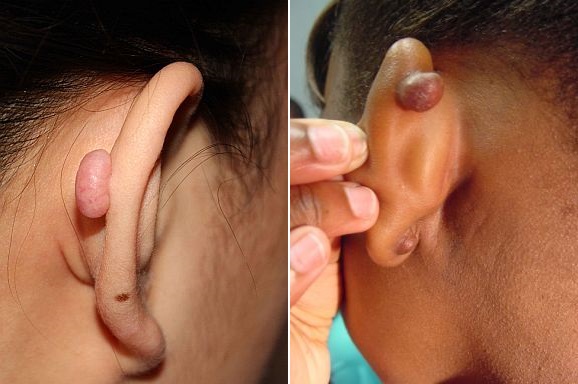
Cartilage piercing bump behind the ear together with a pea sized lump behind the ear lobe.
-
Advertisement

 Facebook
Facebook  Twitter
Twitter  RSS
RSS







